Guest editor: John Tranter
Guest editor: John Tranter
Series editors: Bronwyn Lea and Martin Duwell
The editor of this, the fifth volume in our series does, literally, need no introduction, at least for most readers of Australian poetry. Since the mid-sixties John Tranter has been a continuous, modernising force in our poetry and, more recently, risen to the point where he is acknowledged as one of a select few of Australia’s really great poets. His poetry, as shown in his most recent New and Selected poems, Urban Myths (UQP, 2006), is a complex mix of abstraction and concreteness (he writes as well about the ambience of Sydney, his home town, as any poet), experiment and nostalgia (it is remarkable how often the rural world of his adolescence emerges in the poems). He is also a formal master, reinvigorating old forms and inventing new ones. It is worth noting that Tranter has also been an editor of and for magazines. At the moment he is the editor of an online journal, Jacket, which many people have thought – and said – is the best of its kind in the world.
Perhaps less well-known is the fact that Tranter is an anthologist of real importance. Most will know of his anthology of the group of poets to which, in terms of literary history, he belongs, The New Australian Poetry (Makar, 1979) and of his editing, with Philip Mead, The Penguin Book of Modern Australian Poetry (Penguin, 1991). The second of these surprised many readers, who perhaps feared a stony-hearted, experimental rigorousness, by its generous inclusiveness. Less well-known are Tranter’s Preface to the Seventies – a prescient selection of new poets published by Poetry Australia – and The Tin Wash Dish (ABC, 1989) – a selection of poems made from entries in a bi-centennial competition run jointly by the Australian Broadcasting Corporation and the Australian Bicentennial Authority. Again, what stood out, was its editor’s love of poetry and of the surprises it can bring. As he says:
I saw a chance to compile a genuinely democratic collection of poems by all sorts of Australians, all living and writing in the late 1980s, about every theme imaginable, in every style and form under the Australian sun. Perhaps it’s only now, at the beginning of the third century of white colonisation, when we have learnt to face the often unpleasant facts of our history and the difficult compromises of our social and cultural mix, that an authentic Australian voice can begin to be heard. If so it’s a voice rich with diversity.
‘Rich with diversity’ sounds very like the keynote of The Best Australian Poetry 2007.
All poems are built along an axis with Life at one end and Art at the other. Some – Tranter’s own work is an example, as is Robert Adamson’s, though in a very different way – negotiate this binary with more complexity than others. Some seem to speak simply about, to represent, the world but are in acknowledged or unacknowledged ways verbal creations true to laws which are the laws or art not the world. Others may take the inside of the mind as their subject – meditations – but are never entirely divorced from the world – which is, after all, if nothing else, the home of their metaphors. Others attempt to be entirely referential, to live inside the world of art or its equally complicated friend, language, but even the most abstract or self-referential of works is an object in the world. Many readers of this anthology will expect from someone with Tranter’s reputation as a high postmodernist an anthology of poems leaning towards the ‘art’ end of the spectrum. They will be surprised. There are many powerful poems here deeply concerned with life as it is lived. In the case of a poem like Pam Brown’s ‘Darkenings’ this involves a rapid sketching of an immediately apprehended reality. Michael Sharkey’s brilliant ‘The Land of Eternal Verities’ is a comic meditation on generational relationships in a distorted but recognizable Australia and Reg Mombassa’s ‘A Commemorative Tone Poem of Surprising Delicacy’ is also in a high comic/hyperbolic mode. But poems like joanne burns’ ‘fork’, John Millett’s ‘Elderly Woman at the Financial Planners’, Megan Petrie’s ‘Peter Doyle’, Brendan Ryan’s ‘What It Feels Like’, Mary Jenkins’ ‘In Tidy Town’ or Cath Keneally’s ‘Crying Girl’ or, indeed, a number of others, derive from a kind of quiet but insistent social-justice tradition in Australian poetry in that they record events and scenes with social implications. Underneath this surprisingly large representation you can feel, I think, Tranter’s abiding interest in the voices of poetry as social and cultural phenomena, intriguingly diverse and, at their best, never drab, predictable or pontifical.
The book opens with an elegant meditation about art in Robert Adamson’s ‘Double-Eyed Fig Parrot’ where that fantastic bird seems an icon of poetry itself looking simultaneously at life and at art. The fact that our anthologies are organised so that the authors appear in alphabetical order produces the accident that the Adamson poem is followed by Judith Bishop’s ‘Still Life with Cockles and Shells’ a work that seems almost to be a counterpart. Here the life is in the art, not the reality of the dead subjects. The poem speculates about the implications of life arising from the dead and finishes with two visions of the end of the world when we are all, paradoxically, dead but still alive. Barbara Fisher’s ‘The Poet’s Sister’ concerns itself with Dorothy Wordsworth’s interaction with her brother and though it may be, at one level, an attempt to recover the reputation of an important and unjustly silenced figure, the level that intrigues us is where Wordsworth’s ‘The Daffodils’, in pretending to be a solitary’s experience, is built upon a lie.
There are a number of meditative poems too in this collection ranging from Chris Wallace-Crabbe’s ‘A Vocation’ which is a kind of audit of his current physical and psychical status (‘The myth I keep on peddling through a life, / That work may be identical to play, / Will do me after all’) to Jennifer Harrison’s ‘Baldanders’ – a difficult but impressive meditation on mirrors and their capacity to, at any moment, be ‘something else’, “Baldanders”. Finally there is Clive James’ ‘A Gyre from Brother Jack’ which, despite being an unlikely candidate, seems quite central to this collection. It compares the two brothers Yeats – one as poet the other a painter – opting for the artist rather than his far more celebrated brother. What James finds in a single painting of by Jack Yeats, ‘A Morning Long Ago’, is a registration of life, not in mundane details but in the realized drama of just how meagre our time on earth is:
William had theories, Jack had just the thrill.
We see a little but we miss the rest,
And what we keep to ponder, time will kill.
…
The only realistic general scheme
Of the divine is in this rich display –
Proof that the incandescent present tense
Is made eternal by our transience.
It is a fine meditation on art and its complex interactions with the process of living.
♦
Last year’s anthology, The Best Australian Poetry 2006, had already gone to print when that year’s guest editor, Judith Beveridge, wrote to tell us that her good friend, poet Vera Newsom, had died on 10 July 2006. It was therefore not possible at the time for Beveridge to acknowledge the loss in these pages. And so we do it now. Newsom began publishing poetry in Australian literary magazines in the early 1980s and her first collection, Midnight Snow, was published in 1988 at the age of 76. Newsom published three further collections of poetry, including the award-winning Emily Bronte Recollects. At a celebration for Newsom’s 90th birthday in 2002, Beveridge delivered an address in which she described Newsom’s poetry as ‘characterised by a meticulous attention to craft, to clarity, to directness, to rhythm, to a sparse lyrical elegance, and by a deft tonal and formal control’. In 2003 Newsome was awarded a Medal of the Order of Australia (OAM) for service to literature as a poet and through her support for the emerging talent of other writers. At the time of her death, Newsom was working with Beveridge and other friends to produce a volume of new and selected poems to be published by Five Islands Press. 2006 was also the year in which Lisa Bellear, a Goernpil woman of the Noonuccal people of Minjerribah (Stradbroke Island), died. As well as being a poet, Bellear – author of Dreaming in Urban Areas (UQP, 1996) – was a visual artist, academic and social commentator actively engaged in Indigenous affairs throughout Australia.
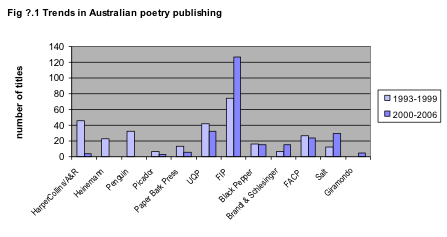
From poets to poetry presses: two of Australia’s smaller publishing houses announced a change focus for 2007: Pandanus Books, based at the Australian National University, ended its poetry publishing days in 2006 with Windchimes: Asia in Australian Poetry, an anthology comprising poems that offer perspectives on Asia by eighty-six Australian poets; and feminist publisher, Spinifex Press, stopped publishing new books altogether. Five Islands Press – with the retirement of founder Ron Pretty – also announced a change of focus, dropping its New Poets Program (which published 32-page chapbooks by six emerging poets each year) and streamlining its mainstream program. From time to time, the New Poets Program had been criticised for being too large to maintain a consistently high quality, nevertheless it launched the careers of a number of 1990s poets who went on to enjoy critical success – Peter Minter and MTC Cronin among them – in much the same way as the Gargoyle Poets series did for Australian poets in the 1970s. It is sad to see it go.
Fortunately, a few small presses have risen to fill the gaps: David Musgrave’s Puncher & Wattmann, which started modestly with one title in 2005, kicked into full swing in 2006 with the publication of three new poetry titles; Paul Hardacre’s papertiger media launched its attractive Soi 3 Modern Poets imprint in 2006; and the eponymous John Leonard Press, producing books noted for top quality production, unveiled a promising list with four poetry books in 2006 and six in 2007. Which goes some way toward ensuring that the poetry book, while doing it tough in the current publishing climate, will not entirely disappear from bookshelves.
We made mention earlier of our guest editor’s role as the editor of an online journal. Taking off in the late nineties, online poetry journals have offered a new world of opportunity for editors not wanting (or unable) to finance expensive print journals. Tranter’s Jacket, launched in 1997, was one of the earliest and has become the most eminent, bringing into conversation poets and critics from around the world. At reportedly over half-a-million hits since its inception, it is difficult to imagine a poetry journal in print format attracting a comparable amount of traffic. A short list of other Australian-based, online poetry magazines that have steadily grown in profile might include Cordite, Divan, Retort, Stylus Poetry Journal, hutt and foame:e. Since we monitor each year the ground rules for our anthology, we have updated our initial decision to avoid taking poems from electronic journals. In coming anthologies, we intend to add the best of these sites to our list of literary magazines from which we source the year’s best poems.
 In everyday scale, a letter of the alphabet is usually no bigger than a freckle or an iris, and a word is not much wider than a thumbnail. The tiny components of written language are rendered almost invisible to us in our race to extract all-important ‘meaning’. But in concrete poetry, language stands in our way: letters and words fight – through scale or arrangement – for visibility. As Roberto Simanowski puts it: ‘concrete poetry deals with the relation between the visible form and the intellectual substance of words’. It is visual, he says, because it ‘adds the optical gesture of the word to its semantic meaning’. As a consequence, concrete poems ask readers to look simultaneously ‘at’ and ‘through’ language.
In everyday scale, a letter of the alphabet is usually no bigger than a freckle or an iris, and a word is not much wider than a thumbnail. The tiny components of written language are rendered almost invisible to us in our race to extract all-important ‘meaning’. But in concrete poetry, language stands in our way: letters and words fight – through scale or arrangement – for visibility. As Roberto Simanowski puts it: ‘concrete poetry deals with the relation between the visible form and the intellectual substance of words’. It is visual, he says, because it ‘adds the optical gesture of the word to its semantic meaning’. As a consequence, concrete poems ask readers to look simultaneously ‘at’ and ‘through’ language.